what is intestinal permeability test|increased intestinal permeability symptoms : discounter We already know that increased intestinal permeability plays a role in certain gastrointestinal conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and irritable bowel syndrome. The biggest question is whether or not a leaky . WEBDurante a gestação, ocorre fisiologicamente a liberação de pequena quantidade de DNA do feto na circulação sanguínea materna. Assim, através da análise de uma amostra de sangue da mãe é possível determinar o sexo do feto, a partir da pesquisa de regiões do cromossomo Y nesse material.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB7 de fev. de 2024 · Tutorial Download. Entra na U.A High, uma escola para treinar a próxima geração de heróis e heroínas! Embora nosso herói não tenha se matriculado apenas para assistir a algumas aulas, alguns segredos estranhos estão sob a superfície da escola – começando com o misterioso destino de seu pai. Desbloqueie todo o potencial .
Leaky gut syndrome is a hypothetical condition. It’s based on the concept of relative intestinal permeability. See moreThere are diseases that are known to be associated with intestinal permeability, and there is a lot of speculation about other possible diseases that might be . See moreThe known causes of intestinal permeability involve systematic erosion of the intestinal lining. This is not a simple feat. Your intestinal lining has many layers of . See moreErosion of your intestinal lining is one thing, and intestinal permeability is another. Most people who think they may have a leaky gut have certain common . See more
We already know that increased intestinal permeability plays a role in certain gastrointestinal conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and irritable bowel syndrome. The biggest question is whether or not a leaky .
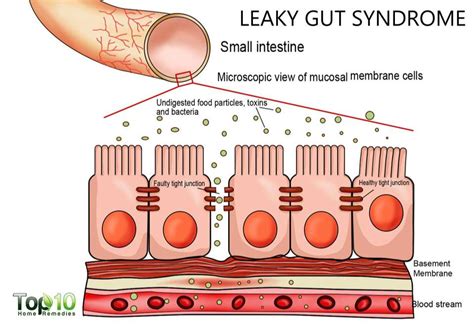
If you’re concerned you might have a leaky gut, aka intestinal permeability, you might be considering getting tested. However, blood, stool, and urine tests can be expensive . When it comes to assessing if a patient has Intestinal Hyper-Permeability, or Intestinal Barrier Penetration, a.k.a. “Leaky Gut”, there are currently only a handful of reliable lab tests that are used. Made up of a single layer of epithelial cells connected by tight junction proteins, it carefully allows water and nutrients to pass into the bloodstream while blocking potentially harmful particles like undigested food, .
Certain symptoms are related to leaky gut (or increased intestinal permeability). However, leaky gut syndrome itself isn't a recognized medical condition. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea.
Intestinal Permeability. A possible cause of leaky gut is increased intestinal permeability or intestinal hyperpermeability. Several diagnostic tests can help identify increased intestinal permeability. The lactulose-mannitol test measures the absorption of two non-metabolized sugars (lactulose . Leaky gut is the idea that increased permeability of the intestine allows toxins and bacteria to enter the body, potentially leading to inflammation and other symptoms. There is no accepted way to diagnose or treat leaky gut syndrome. However, the gut can become more permeable, leading to a risk of symptoms inside and outside of the .
While test-tube studies have found that gluten can increase intestinal permeability, human-based studies have not observed the same effect (10, 11, 12). Aside from zonulin, other factors can also .A stool analysis assesses digestive function, intestinal inflammation, and the intestinal microbiome, which may contribute to symptoms. In addition to common gastrointestinal complaints, clinicians often assess gut health for numerous . In future, LM test to assess intestinal permeability in children can be simplified by shortening the urine collection time from 5 hours to 2 hours. Introduction. The lactulose: mannitol (LM) test is a quantitative assay for directly measuring the ability of two non-metabolized sugar molecules—lactulose and mannitol—to permeate the . No test is universally recognized as reliable in diagnosing intestinal permeability. Some specialized testing is being studied, but there isn't enough information yet to use these tests in patients with any certainty. . Probiotics that contain two different strains of a bacteria called Bifidobacterium helped these people with intestinal .
Leaky gut syndrome is the theory that increased permeability of the GI tract to toxins leads to various symptoms and inflammatory conditions.
what causes increased intestinal permeability
intestinal permeability test kit
Intestinal barrier permeability may therefore be a prognostic marker for disease pathophysiology; similarly, targeting the intestinal barrier permeability holds promise for therapy and for the .
Intestinal permeability tests mostly are used in studies of the pathophysiology of intestinal disorders; they do not provide a specific diagnosis. 138. . Plasma values and/or urinary excretion of the test compound are measured, and so results are influenced by renal function. Increased permeability of the gut is a nonspecific finding in .
Intestinal permeability, often referred to as "leaky gut syndrome," is a condition that has garnered significant attention in both medical research and popular health discussions. . Symptoms and Diagnostic Testing. Symptoms of intestinal permeability are diverse and can affect various bodily systems. Common symptoms include digestive issues .
Using a collection of innovative biomarkers, this test helps clinicians determine if their patients have intestinal permeability, or “leaky gut.” Intestinal permeability has been suggested as a root cause of autoimmune diseases, systemic inflammation, and food sensitivities.
The objectives of this review on 'leaky gut' for clinicians are to discuss the components of the intestinal barrier, the diverse measurements of intestinal permeability, their perturbation in non-inflammatory 'stressed states' and the impact of treatment with dietary factors. Information on .To test for these levels, I recommend the Histamine and Intestinal Permeability Test. This is a comprehensive test that tests for histamine, DAO, the DAO: Histamine ratio, Zonulin, and Lipopolysaccharide (LPS). With the help of this test, you can find out if you have histamine intolerance and look for signs and risk factors of intestinal . Increased intestinal permeability is associated with conditions like inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and celiac disease. Signs and symptoms. Doctors associate several symptoms with increased intestinal permeability. Still, there’s currently not much evidence that increased permeability is the cause of these .in the intestinal permeability test [4–6, 8, 9]. E.g., in a study by Ahmed and colleagues, the DIO mice gained 130% of their initial weight while the lean mice gained 30%, and the DIO mice
Stool Zonulin Test. Method: A stool sample is collected and tested for zonulin. What it Shows: Measures zonulin directly in the gut lumen, providing a localized assessment of gut permeability.High levels suggest that your gut lining is more permeable than it should be. Advantages: The Gut Zoomer and GI-MAP tests measure Zonulin, plus they also measure .Measures intestinal permeability to large molecules, which inflame the immune system. The Array 2 helps practitioners narrow his/her focus in identifying triggers that need to be removed and choose a more effective, personalized, gut healing protocol.
Data are accumulating that emphasize the important role of the intestinal barrier and intestinal permeability for health and disease. However, these terms are poorly defined, their assessment is a matter of debate, and . Background A widely used method in assessing small bowel permeability is the lactulose:mannitol test, where the lactulose:mannitol ratio (LMR) is measured. However, there is discrepancy in how the test is conducted and in the values of LMR obtained across studies. This meta-analysis aims to determine LMR in healthy subjects, coeliac and Crohn’s disease. . The differential sugar absorption test is considered the “gold standard” method for functional small intestinal permeability testing. Under normal conditions, large oligosaccharides like lactulose should not be able to traverse the intestinal barrier, while small monosaccharides like mannitol or rhamnose should be able to pass across freely
The role of intestinal permeability in the pathogenesis of immune-mediated diseases is a relatively new field of translational science that only recently has received proper attention. While the zonulin pathway is the only physiologic mechanism described so far, it is likely that other pathways are involved in physiologic TJ modulation. .Intestinal Permeability Assessment Interpretation Guide There are two primary methods used clinically to assess leaky gut: the lactulose/mannitol . covered in another handout). The lactulose/mannitol test measures levels of both sugars in a patient’s urine after oral ingestion. Lactulose and mannitol are both oligosaccharides. Their .Removal of this agent prompts complete remission of all attributes of the disease, including a return of abnormal intestinal permeability to almost the normal range in the majority of subjects. 78 In fact, an increase in permeability is a sensitive test for the presence of even small amounts of gluten in the diet. 78 However, if intestinal .

Created Date: 5/28/2021 10:12:23 AMThe objectives of this review on ‘leaky gut’ for clinicians are to discuss the components of the intestinal barrier, the diverse measurements of intestinal permeability, their perturbation in non-inflammatory ‘stressed states’ and the impact of treatment with dietary factors. Information on ‘healthy’ or ‘leaky’ gut in the public domain requires confirmation before endorsing .
Testing of intestinal permeability is not required for routine patient care, however it is an important tool to understand the function of the paracellular transport in the research setting. Increase in intestinal permeability has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases including celiac disease, Crohn's disease, type I .
Intestinal permeability is a term describing the control of material passing from inside the gastrointestinal tract through the cells lining the gut wall, into the rest of the body.The intestine normally exhibits some permeability, which allows nutrients to pass through the gut, while also maintaining a barrier function to keep potentially harmful substances (such as antigens) from . Nevertheless, medical professionals do agree that increased intestinal permeability, or intestinal hyperpermeability, exists in certain chronic diseases (1, 2). Summary: An intestinal permeability assessment can also measure the ability of two sugar molecules to permeate the gut lining — lactulose and mannitol. This leaky gut test checks for levels of the two sugars present in the urine from a sample collected over the six hours after ingesting them. 2. IgG Food Intolerance Test. Why It’s Important:
intestinal permeability test at home
intestinal antigenic permeability screen
Jewel Star. Casual Classic Puzzle Windows version brought to you by Rolling Donut Apps. Connect 3 or more jewels together to make them disappear. Match lightning, blast, and star jewels for bigger bonuses and combos. With easy to use controls, fun and friendly graphics, and over 200 levels to play, this game is fun for the whole family!
what is intestinal permeability test|increased intestinal permeability symptoms